Geriatric Behavioral Health: Services and Approaches. Discover essential geriatric behavioral health services & approaches designed To support seniors. Learn how compassionate care enhances wellbeing & quality of life.
What is Geriatric Behavioral Health: Services & Approaches & how does it work?
Geriatric behavioral health focuses on mental well-being. It serves elderly individuals with various emotional concerns. This field acknowledges how aging impacts mental health. Services often include assessments. Therapy, & medication management.
Brief history of Geriatric Behavioral Health: Services & Approaches
Geriatric behavioral health evolved from traditional psychiatry. Early recognition of unique needs in elderly populations spurred development. Over decades. Specialists created tailored services for this demographic. Increased awareness led communities toward improved support systems.
How To implement Geriatric Behavioral Health: Services & Approaches effectively
Implementing effective services requires collaboration among professionals. Each team member should understand geriatric-specific needs. Regular training enhances skills in elderly psychological care. Assessment tools help identify underlying issues accurately.
Key benefits of using Geriatric Behavioral Health: Services & Approaches
Improved mental health results from targeted interventions. Support systems foster emotional resilience among seniors. Enhanced quality of life emerges through tailored therapies. Family involvement boosts treatment adherence & effectiveness.
Challenges with Geriatric Behavioral Health: Services & Approaches & potential solutions
Challenges include stigma associated with mental health. Low awareness often prevents seniors from seeking help. Accessibility remains an issue for some communities. Solutions involve outreach programs & education initiatives aimed at demystifying mental health services.
Future of Geriatric Behavioral Health: Services & Approaches
Future trends prioritize integrative care models. Technology will enhance communication among healthcare providers. Telehealth services will simplify access for remote individuals. Focus will shift towards preventive mental health strategies for seniors.
Table of Geriatric Behavioral Health: Services & Approaches
| Service | Description |
|---|---|
| Assessment | Initial evaluation of mental health status |
| Therapy | Individual or group therapy sessions |
| Medication | Management of psychiatric medications |
| Support Groups | Peer support for shared experiences |
| Family Counseling | Engagement of family in treatment process |
Understanding Geriatric Behavioral Health
Geriatric behavioral health focuses on mental wellness for older adults. Senior individuals often face unique psychological issues. Factors like chronic illness. Isolation, & loss contribute significantly. Addressing these concerns requires specialized services. These services enhance overall quality of life for older adults. Comprehensive approaches target mental. Emotional, & social wellbeing of seniors. Through tailored interventions. Care providers nurture healthier aging processes.
Research highlights how mental health influences geriatric populations. Studies show that untreated mental health issues can exacerbate physical health concerns. A link providing additional insights can be found here. Mental health problems such as depression & anxiety can lead To increased disability. These complications can severely impact dayToday functioning. Consequently. A strong focus on behavioral health becomes essential in geriatric care.
Practitioners must incorporate a holistic perspective. Each individual requires a tailored approach addressing specific needs. Professionals utilize various methods. Including psychotherapy & medication. Aimed at promoting mental wellness. Recognizing these needs ensures a more effective intervention. Collaboration among healthcare providers strengthens outcomes for seniors. Therefore. An integrated team approach fosters comprehensive care.
Common Challenges in Geriatric Behavioral Health
Cognitive Decline
Cognitive decline affects many older adults. This decline can manifest as memory loss or difficulty with concentration. Conditions such as Alzheimer’s & other dementias often contribute significantly. Research suggests cognitive impairment correlates with depression & anxiety. Thus. Recognizing symptoms early becomes crucial for appropriate interventions. Support systems must focus on enhancing cognitive function whenever possible.
Various cognitive therapies exist that can assist. For example. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) often proves effective. This method helps patients identify negative thoughts & patterns. Through teaching coping strategies. Individuals can experience improved mental states. Diagnostic assessments identify individuals who might benefit from cognitive interventions.
Often. Families may struggle when caring for a loved one with cognitive decline. They might experience feelings of helplessness. Which can lead To burnout. Providing education & support for caregivers enhances their ability To manage challenges. Implementing support programs can foster resilience in caregivers. Ensuring they remain equipped. Stronger support networks help maintain effective caregiving practices.
Depression & Anxiety
Depression ranks among most common mental health issues affecting seniors. Many factors contribute. Such as loss of loved ones or health deterioration. Symptoms may manifest as sadness. Fatigue. Or changes in sleep patterns. Anxiety. Too. Affects numerous seniors. Often stemming from fears of mortality & illness. Recognizing these symptoms is vital for timely interventions & treatment.
Therapeutic approaches can effectively alleviate symptoms. Psychotherapy options. Such as CBT & interpersonal therapy. Focus on underlying thoughts & emotions. Medication management may complement therapy. Enhancing effects of treatment. Careful monitoring must accompany any medication prescribed. Particularly due To potential side effects.
Creating support groups for seniors can foster connection. These may help individuals share experiences & build resilience. Engaging socially leads To positive mental health outcomes for older adults. Connections with peers bolster community ties that diminish isolation. Strengthening relationships enhances overall wellbeing for seniors.
Importance of Screening & Assessment
Regular Mental Health Screenings
Seniors must undergo regular mental health screenings. These screenings serve as assessments that identify potential issues early. Early detection facilitates timely intervention. Often improving outcomes significantly. Health professionals should screen for common conditions. Such as depression or anxiety. Screening ensures a proactive approach To managing mental health needs.
Multiple tools exist for conducting effective screenings. Standardized questionnaires can provide valuable insights. Trained professionals can utilize tools like The Geriatric Depression Scale. Additionally. Incorporating family members into assessments can help reveal underlying issues. Family perspectives often highlight areas not immediately visible To practitioners.
Regular assessments create an ongoing dialogue about mental health. As seniors age. Needs may evolve. Necessitating adjustments in care. Continuous evaluations empower care providers with essential information. Providers can then tailor interventions that adapt over time. This flexibility enhances The effectiveness of behavioral health services.
Intervention Strategies in Geriatric Behavioral Health
Psychotherapy Approaches
Psychotherapy stands as a primary intervention strategy. Older adults can benefit significantly from various modalities. Cognitive behavioral therapy often ranks high for effectiveness. This method targets negative thought patterns. Promoting healthier thinking. Therapists work collaboratively with clients. Ensuring active participation throughout treatment.
Other modalities. Such as reminiscence therapy. Encourage sharing life stories. This therapy helps older adults reflect on their lives. Fostering a sense of purpose. Incorporating reminiscence invites exploration of memories. Contributing To stronger selfidentity. Acknowledging past experiences often promotes emotional healing.
Group therapy also offers substantial benefits. Connecting with peers provides an avenue for social support. Sharing experiences within a group setting encourages bonding. Participants often realize they are not alone in their struggles. Such realizations foster a sense of community that enhances healing.
Medication Management
Medication management plays an essential role in behavioral health. Proper diagnosis leads To appropriate medication choices. Prescribing antidepressants or anxiolytics may prove beneficial for specific conditions. Monitoring these medications closely remains crucial due To potential side effects. Frequent communication between health providers ensures optimal management of prescribed drugs.
Clinical guidelines can assist with medication prescriptions. Practitioners must always consider potential drug interactions. Older adults frequently take multiple medications for various health issues. Reviewing current prescriptions helps mitigate adverse effects & unnecessary complications. Continual assessment may reveal whether medication adjustments are required.
Educating patients about medications fosters adherence. Engaging discussions around potential side effects & benefits promote informed decisions. Ensuring patients understand their treatment plans strengthens clientprovider trust. Establishing effective communication channels leads To better adherence & ultimately improved outcomes.
Integration of Care in Geriatric Behavioral Health
Multidisciplinary Teams
Integrating care through multidisciplinary teams promotes holistic wellness. Healthcare providers across multiple disciplines collaborate effectively. Psychiatrists. Psychologists. Social workers, & primary care doctors form essential components of a care team. Each professional leverages unique skills To address diverse needs. This collaboration strengthens service provision. Enhancing care outcomes significantly.
Effective communication within these teams catalyzes better coordination. Regular meetings allow providers To discuss patient progress & concerns. Sharing insights ensures all team members remain informed. Discussions help identify emerging needs that may require adjustments in treatment. Enhanced coordination leads To a unified approach & improved patient experience.
Teamoriented care often yields beneficial outcomes for clients. Older adults respond positively when care aligns with their unique needs. The collaborative environment nurtures a support network essential for seniors. As caregivers strengthen ties. Clients experience an overall enhanced quality of care.
Social Engagement & Community Resources
Importance of Social Connections
Social engagement significantly influences mental wellbeing. Strong social connections often lead To improved emotional health. Seniors with active social lives experience lower rates of depression & anxiety. Engaging in community activities fosters meaningful relationships. These connections serve as vital lifelines that enrich lives.
Community resources play a critical role in maintaining social engagement. Local organizations often provide recreational & support activities specifically tailored for seniors. Many local centers offer classes. Workshops, & social events that invite participation. Gaining access To these resources encourages seniors To remain connected.
Implementation of technology can also enhance social connections. Virtual platforms allow seniors To engage with loved ones regularly. Online groups help those who might struggle with mobility issues participate in communities. Participating digitally opens doors for varied social interactions. This adaptability fosters friendships & connections that promote mental wellness.
Family Involvement in Geriatric Behavioral Health
Support for Family Caregivers
Family involvement often proves critical in supporting senior mental health. Ensuring caregivers receive necessary resources enhances their ability To provide care. Informing families about mental health issues becomes paramount. Education empowers them. Equipping them with tools for understanding specific needs.
Regular family meetings allow caregivers & health providers To communicate. These discussions facilitate clear channels of information sharing. Conversations regarding treatment plans. Expectations, & concerns lead To collaborative goals. Encouraging open dialogue promotes teamwork in meeting elderly individuals’ needs.
Counseling support for families may alleviate tensions. Family therapy sessions promote shared experiences & foster healing. Understanding each person’s struggles provides valuable perspectives. Empowering families ensures resilience & proactive approaches within caregiving roles. Strengthening these relationships mitigates feelings of isolation among family members.
Future Trends in Geriatric Behavioral Health
Technological Innovations
Technological advancements will significantly influence geriatric behavioral health. Innovations create new opportunities for assessment & intervention. Telehealth options ensure remote access for elderly individuals. Older adults can receive care from home. Accessing needed services. Teletherapy options often improve compliance for seniors reluctant To attend inperson sessions.
Wearable technology increasingly plays a role in health monitoring. Devices can track vital signs. Medication adherence, & emotional wellbeing. Health professionals can remotely monitor data To identify emerging issues. These insights allow caregivers To act proactively. Addressing problems before escalation occurs.
Mobile applications providing mental health resources are gaining popularity. Many seniors increasingly utilize userfriendly applications. These platforms offer coping strategies. Mindfulness exercises, & therapy resources. As technology continues evolving. It becomes more integrated into daily living for seniors.
Challenges in Geriatric Behavioral Health Services
Barriers in Accessing Care
Access To mental health care remains a challenge for many. Geographic barriers limit accessibility for seniors in rural areas. Recognizing these challenges becomes vital for implementing solutions. Telehealth represents one way of bridging these gaps. Ensuring continuity of care.
Transportation issues may exacerbate access challenges for older adults. Many lack reliable means To travel for appointments. Restricting care. Educational outreach can identify local resources that help seniors reach providers. Enhancing community support networks creates better access opportunities.
Affordability often poses additional challenges. While insurance coverage exists. Some may lack sufficient support. Rising healthcare costs can further deter individuals from seeking help. Advocating for improved access To affordable services remains crucial in addressing this gap. Ensuring equitable care promotes healthier aging for all seniors.
Significance of Research in Geriatric Behavioral Health
Advancing Knowledge & Practice
Research plays a critical role in understanding geriatric behavioral health. Ongoing studies lead finetuning interventions that enhance senior care. Exploring new therapeutic methods offers opportunities for improved treatment options. Greater awareness of mental health issues informs better care practices.
Collaboration between researchers & practitioners enhances efficacy. Clinical studies encourage The practical application of findings. Integrating research into standard practice ensures that care remains evidencebased. Continuous improvement remains vital in adapting treatments for seniors effectively.
Involvement in expansive research initiatives raises awareness. Communitybased participatory research might engage seniors in their care. Engaging individuals provides direct insights into their experiences. This engagement can drive better missionaligned services. Promoting holistic care.
Promoting WellBeing Through Lifestyle Changes
Encouraging Healthy Lifestyles
Lifestyle changes often positively impact mental wellbeing. Nutritional choices significantly influence physical & mental health. Ensuring seniors maintain balanced diets equips them To manage stress effectively. Addressing nutrition enhances overall wellness for aging individuals.
Physical activity boasts numerous benefits for mental health. Exercise boosts mood & reduces symptoms of depression. Engaging in regular activities promotes cognitive function as well. Fitness programs tailored for seniors bolster resilience through improved strength & mobility.
Mental stimulation also remains vital in maintaining cognitive health. Games. Puzzles, & educational classes serve as engaging activities. Encouraging lifelong learning fosters continued engagement with The world. Nurturing curiosity enhances overall quality of life for seniors.
- 🧠 Comprehensive assessments for mental health
- ✔️ Integrated multidisciplinary teams
- 🌐 Telehealth services for accessibility
- 👥 Emotional support through peer groups
- 📚 Continuous education for caregivers
Understanding Grief & Loss in Seniors
Resources for Navigating Grief
Grief profoundly impacts mental health for seniors. Loss of loved ones or familiar environments often stirs strong emotions. Understanding this grieving process allows for effective support mechanisms. Helping older adults navigate loss leads To healthier coping strategies.
Creating safe spaces for expression can facilitate healing. Support groups implemented within communities empower individuals. Sharing experiences fosters shared understanding while alleviating feelings of isolation. Many find comfort in knowing they are not alone.
Professional counseling services can provide essential support. Individuals may benefit from therapists specializing in grief counseling. Such caregivers possess skills To guide seniors through their emotions effectively & compassionately. Enabling seniors To manage grief continues To improve emotional wellbeing.

Understanding Geriatric Behavioral Health
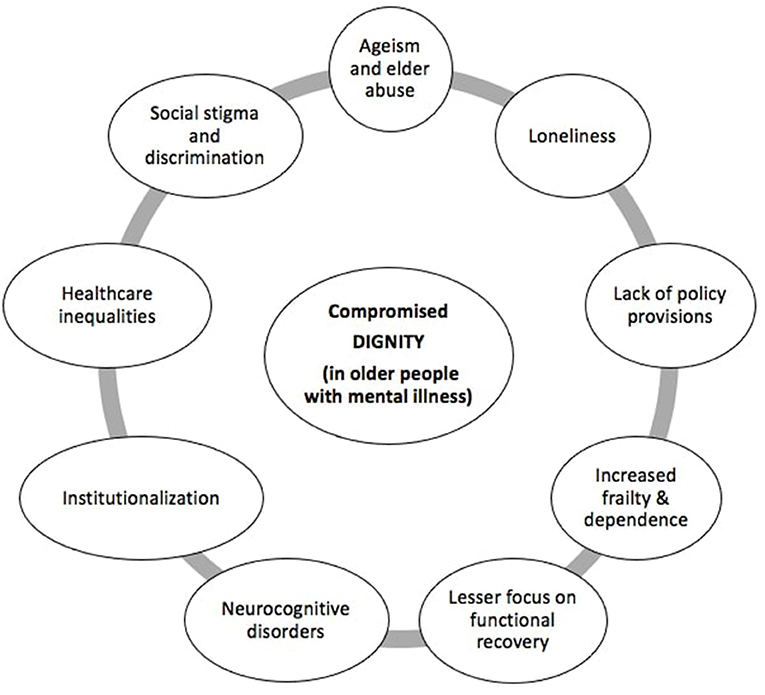
Older adults face unique challenges. Their mental health demands special attention. Aging affects psychological wellbeing. Agerelated issues. Such as dementia or depression. Manifest differently.
Society often overlooks older populations. Many assume these individuals lack psychological care needs. This misconception can delay treatment & worsen conditions. Comprehensive support services must address these facets for effective care.
Senior health relies on a holistic approach. Integrating physical & mental health ensures comprehensive wellbeing. Collaboration among healthcare professionals fosters effective care plans. Families also play vital roles in supporting older adults.
Unique Behavioral Health Concerns
Various behavioral health issues arise among older adults. Common conditions include anxiety. Depression, & substance abuse. Unacknowledged grief may impact their mental state. Addressing these concerns early can prevent further complications.
Older adults often struggle with cooccurring disorders. For instance. Anxiety can coexist with chronic health issues. These complexities require specialized treatment strategies. [Find more about these challenges](https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33475445/).
Awareness about behavioral health matters greatly. Many seniors feel isolated or misunderstood. Understanding their needs enhances communitydriven care. Programs aimed at increasing awareness can facilitate access.
Services Offered in Geriatric Behavioral Health
Comprehensive services cater specifically To this demographic. Individual therapy. Group therapy, & medication management form core components. Each service targets unique aspects of behavioral health.
Individual therapy creates personalized experiences. Specialists develop custom strategies based on each person’s needs. Group sessions encourage social interaction & shared experiences. Such engagement provides an emotional safety net.
Medication management requires careful oversight. Aging alters medication metabolism. Leading patients at risk for interactions. Regular communication between physicians & patients can optimize treatment outcomes. [Explore further information on this topic](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9453913/).
Approaches in Geriatric Behavioral Health
Behavioral health approaches should remain flexible. Professionals must adapt treatments. Using various modalities. Common approaches include cognitivebehavioral therapy. Mindfulness techniques, & supportive counseling.
Cognitivebehavioral therapy (CBT) offers proven benefits. It helps patients reframe negative thoughts. Many seniors experience improved mental health through structured sessions.
Mindfulness & relaxation techniques can reduce anxiety. These approaches promote emotional regulation & peace. Coupling these practices with traditional therapy provides a comprehensive treatment plan.
Role of Family & Caregivers
Family members influence behavioral health support significantly. A supportive environment boosts mental wellbeing. Caregivers often encounter challenges while managing older adults’ needs.
Open communication fosters stronger relationships. Families can educate themselves about mental health resources. Encouraging older adults To participate in support groups can enhance social connections.
Recognizing caregiver fatigue remains critical. Support programs for caregivers alleviate stress. These initiatives maintain a healthy dynamic between patients & caregivers.
Assessment & Diagnosis
Comprehensive assessments provide vital information. Assessments include clinical interviews & questionnaires. It allows practitioners To gauge mental health status accurately.
Diagnosing behavior health conditions in older adults presents challenges. Symptoms may mimic other health issues. Professionals need thorough evaluations for correct diagnosis.
Diagnostic criteria must adapt as new understandings emerge. Ongoing education among healthcare providers ensures contemporary practice standards. Professionals can utilize resources like training sessions & continued education.
Comparison of Services & Approaches
| Service/Approach | Description | Target Population | Effectiveness | Emojis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Individual Therapy | Personalized treatment plans | Seniors with specific issues | High | 🧑⚕️ |
| Group Therapy | Support from peers | Seniors experiencing isolation | Moderate | 👥 |
| Medication Management | Oversight of prescriptions | All older adults | High | 💊 |
| CognitiveBehavioral Therapy | Mental reframing tactics | Seniors with depression | High | 🧠 |
| Mindfulness Approaches | Promotes relaxation | All older adults | Moderate | 🧘♂️ |
Experience & Implementation
In my professional journey. I witnessed significant transformations. Seniors expressed gratitude for obtained behavioral support. Changes resulted from personalized approaches & dedicated interventions.
I regularly participated in community outreach programs. These encounters enhanced relationships with older adults. Each connection held its unique story. Leaving lasting impressions.
Through sharing experiences. I learned valuable lessons. Understanding geriatric behavioral health became my calling. Every individual’s journey contributes To a collective understanding.
What is geriatric behavioral health?
Geriatric behavioral health focuses on The mental & emotional wellbeing of older adults. Addressing issues like depression. Anxiety, & cognitive decline through specialized therapeutic approaches.
What types of services are available in geriatric behavioral health?
Services may include individual therapy. Family counseling. Medication management. Group therapy, & support programs tailored specifically for seniors.
How can therapy benefit older adults?
Therapy can provide older adults with tools To cope with life changes. Improve communication skills. Manage depression or anxiety, & enhance overall quality of life.
What role does medication play in geriatric behavioral health?
Medication can help manage symptoms of mental health disorders when prescribed by a healthcare professional. Ensuring that treatment is safe & appropriate for older adults.
How is cognitive decline addressed in geriatric behavioral health?
Specialized therapies & interventions. Such as cognitivebehavioral therapy & reminiscence therapy. Can support cognitive function & provide coping strategies for those experiencing memory loss.
What is The importance of family involvement in treatment?
Involving family members can enhance communication. Provide support, & help caregivers understand The challenges faced by their loved ones. Fostering a collaborative treatment approach.
Are there specific challenges faced by older adults in behavioral health?
Yes. Older adults may experience unique challenges such as grief. Isolation. Medical complexities, & agerelated stigma. Which can impact their mental health.
What approaches are taken for treating anxiety in older adults?
Therapeutic approaches can include cognitivebehavioral therapy. Relaxation techniques, & support groups. Tailored To address The specific concerns of older adults.
How does geriatric behavioral health support caregivers?
Support services for caregivers can provide education. Counseling, & respite care. Helping them manage stress & maintain their own mental wellbeing while caring for older adults.
What community resources are available for older adults?
Community resources may include senior centers. Mental health hotlines. Local support groups, & outreach programs specifically designed for The elderly population.
How can social engagement impact mental health in older adults?
Social engagement can significantly improve mental health by reducing feelings of loneliness. Fostering connections, & promoting a sense of belonging among older adults.
What is The role of holistic approaches in geriatric behavioral health?
Holistic approaches may include activities such as art therapy. Music therapy, & mindfulness practices. Which can enhance emotional wellbeing & overall quality of life.
How important is routine & structure for older adults?
Maintaining a routine can help provide stability & predictability. Which is beneficial for mental health & can reduce anxiety & agitation in older adults.
What are The signs that an older adult may need behavioral health services?
Signs may include increased withdrawal from social activities. Changes in mood or behavior. Difficulties in daily functioning, & expressions of hopelessness or despair.
How can mental health assessments help older adults?
Mental health assessments can identify concerns early. Guide treatment plans, & help healthcare providers understand The specific needs & strengths of older adults.
Conclusion
In summary, taking care of The mental health of older adults is really important. Geriatric behavioral health services focus on understanding their unique needs & providing support in a gentle way. Approaches like therapy & medication can help improve their quality of life. It’s essential for caregivers & families To be aware of The signs of mental health issues & seek help when needed. By working together, we can create a caring environment that helps our seniors feel understood & supported. Ultimately, a little compassion goes a long way in ensuring their well-being & happiness.

